Ecology and Habitat
Ecology and Habitat – The Rainforest Gardener
A Keystone Species
Ecology is the study of how species interact with other animals and plants and their physical environment.
The Southern Cassowary is an extremely important species in Far North Queensland’s tropical rainforests. It is the rainforest gardener, a ‘keystone species’ that maintains the balance and diversity of its rainforest home through its role as a seed disperser. The Southern Cassowary’s main food is rainforest fruits, and the gentle treatment of the fruits through the Cassowary’s primitive digestive system means the seeds are passed relatively unharmed and ready for germination in their own “compost heap” of dung!
Cassowaries are known to eat the fruit of at least 238 species of which 149 are woody trees. 45 of these plants have large fruit that are mostly dispersed by the Southern Cassowary over long distances. Please see the table of Cassowary Food Trees (Kooyman, R. Australian Rainforest Database: Royal Botanic Gardens, Sydney; Macquarie University; based on published sources) for more details.
My Poo Grows Trees
 In Queensland’s rainforests Southern Cassowaries are the only native animal capable of dispersing the seeds of large-fruited plants and trees over long distances, ensuring the continued balance and biodiversity of the rainforest plant community. Without Cassowaries these plants and trees would only occur in concentrated pockets around parent trees or in places where dispersal by gravity can occur, such as gullies or the bottom of slopes.
In Queensland’s rainforests Southern Cassowaries are the only native animal capable of dispersing the seeds of large-fruited plants and trees over long distances, ensuring the continued balance and biodiversity of the rainforest plant community. Without Cassowaries these plants and trees would only occur in concentrated pockets around parent trees or in places where dispersal by gravity can occur, such as gullies or the bottom of slopes.
Conserving Cassowaries has flow-on effects for other threatened rainforest species such as the Musky Rat-kangaroos and Spectacled Fruit Bats, for which the fruit also provides a major food source.
Habitat
Southern Cassowaries live primarily in tropical rainforest, but they also use other types of forest such as eucalypt, mangrove, and tea tree. They are also seen on beaches adjacent to these habitats. Like most animals, Cassowaries need access to fresh clean water for drinking … and bathing! Cassowaries may also venture into suburbs and farmland if they are near their territories or at times of food shortages, such as after cyclones when rainforest trees and fruits have been destroyed by wind and rain.
Each adult Cassowary maintains a home range or territory of about 100Ha. The home ranges of males may overlap with each other’s and with those of females. The loss of Cassowary habitat due to farming and residential development in Northern Queensland is affecting the number of Southern Cassowaries the environment can support. The loss of good quality habitat development (degradation) and purchasing of small parcels of land for homes (fragmentation) is also affecting the Cassowary. Birds living in areas of degraded or fragmented, low-quality habitat need larger home ranges and so the environment cannot support as many birds.
Why Wildlife Corridors are Important
A wildlife corridor is an area of habitat connecting wildlife populations separated by human activities or structures 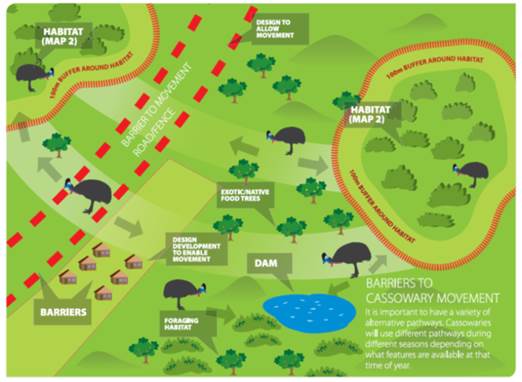 (such as roads, farming, development, or logging). Due to habitat fragmentation, local populations can become dispersed resulting in reduced genetic diversity and inbreeding that often occurs within isolated populations.
(such as roads, farming, development, or logging). Due to habitat fragmentation, local populations can become dispersed resulting in reduced genetic diversity and inbreeding that often occurs within isolated populations.
Creating corridors allows for the reconnection of fragmented habitats and facilitates the re-establishment of populations that may have been affected by fragmentation or eliminated due to random events such as fires or cyclones. Habitat fragmentation due to human development is an ever-increasing threat to biodiversity, and habitat corridors are a possible mitigation. Cassowaries travel across short stretches of open land to feed in rainforest patches, gardens and exotic fruit plantations.
The image above highlights key habitat values including feeding, breeding and resting habitat, water availability and movement corridors. Feeding areas change with fruiting seasons, and traditional food supplies can fail due to events such as cyclones. Cassowary habitat also supports at least 106 plant and 37 animal species identified as threatened under state and federal legislation.
Want to learn more about these incredible birds?
Who am I? The Endangered Southern Cassowary
Indigenous Cultural Significance
Roles of Zoos and Captive Management
Evolution – Where did I come from?


DONATE NOW
When you give generously, you become part of a committed team of individuals who collectively are helping to preserve some of the most biodiverse habitats and the species that live within them on this planet. Become a Rainforest Rescuer today!
purchase
and
protect
>>>
and
protect
>>>


